A graphic card is a chipset that is integrated with the motherboard to render HD GRAPHICS to high-definition monitors like LED, OLED, Super AMOLED, and more, along with graphic rendering on the screen, the Graphic card is utilized for video rendering, video processing, ultra high definition streaming, game rendering, simulations rendering, high computation graphics processing, high fps gaming, and much more graphic intensive workload.
Graphic cards are usually built for both the AMD and intel PROCESSORS but they can be easily expanded for multiple graphic-intensive use cases like gaming, video editors, animation, game rendering, simulators, and much more…The GPU, or graphics processing unit, is a compute expansion card that generates a stream of graphical output. This output is then graphically rendered and displayed via LED, LCD, and OLED monitors. Both the processing and rendering aspects are carried out by the graphics card.
The pixel calculation and Pixel storage for video image data can be very data heavy hence GPU takes all the graphic load and delivers optimized graphical computation and performance. The CPU needs to be powerful enough to be compatible with powerful graphic cards because high data volume needs to stored in the processing buffer and hence the GB of RAM work in sync with the GB of the GPU only of the CPU RAM SIZE is matched with GPU RAM SIZE.
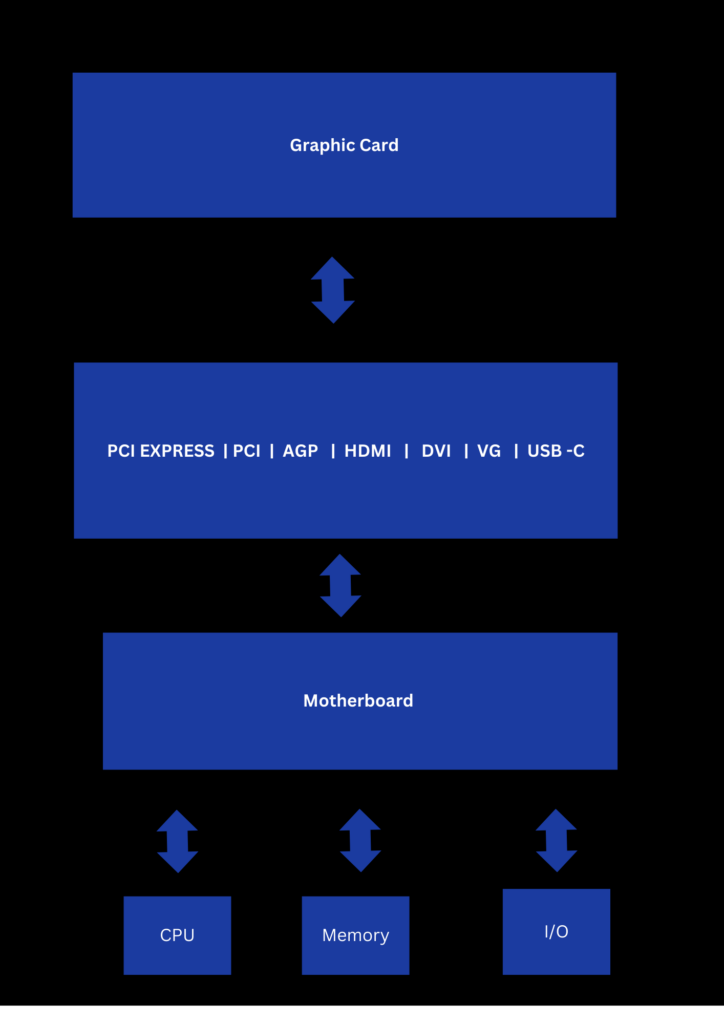
Graphic cards can be connected to the motherboard via
- PCI EXPRESS
- PCI
- AGP
- HDMI
- DVI
- VG
- USB -C
and more connectors are available as the graphical card technology is evolving at a faster pace.
The GPU and CPU works in tandem to carry out processes and hence the graphical rendering and processing load in the CPU is reduced with the help of the GPU.
General-purpose computation will be carried out by the CPU, the pixel calculation and processing-based task will be carried out by the GPU, GPU is PCB-based and is an extension of the computing setup.
The FORM FACTOR of the GPU is measured in height usually GPUs have less height than the PCI SLOTS, and the height to width of GPU is smaller than the PCI SLOTS, it can be around half the size or even lower in some cases.“High-end graphical cards usually occupy two to three expansion slots”
The graphical card can be scaled up by linking them together with the help of a PCIe bus and Bridge. Both AMD and NVIDIA have propriety scaling methods.
SCALING METHODS: for AMD it is CROSS FIRE X | For Nvidia it is SLI.
For operating system performance (3D RENDERING APIs) are available which are leveraged to perform 3D RENDERING.
APIs are:
- VULKAN
- DIRECT X
- METAL
- OPEN GL
- GNMX
The choice of the graphic card is based on the architecture of the processor, the RAM, and the slots, it is advisable to add high-quality RAM and high-quality GPUs and then optimize the performance for best computation, rendering, and processing results.
Diagram
The article above is rendered by integrating outputs of 1 HUMAN AGENT & 3 AI AGENTS, an amalgamation of HGI and AI to serve technology education globally.