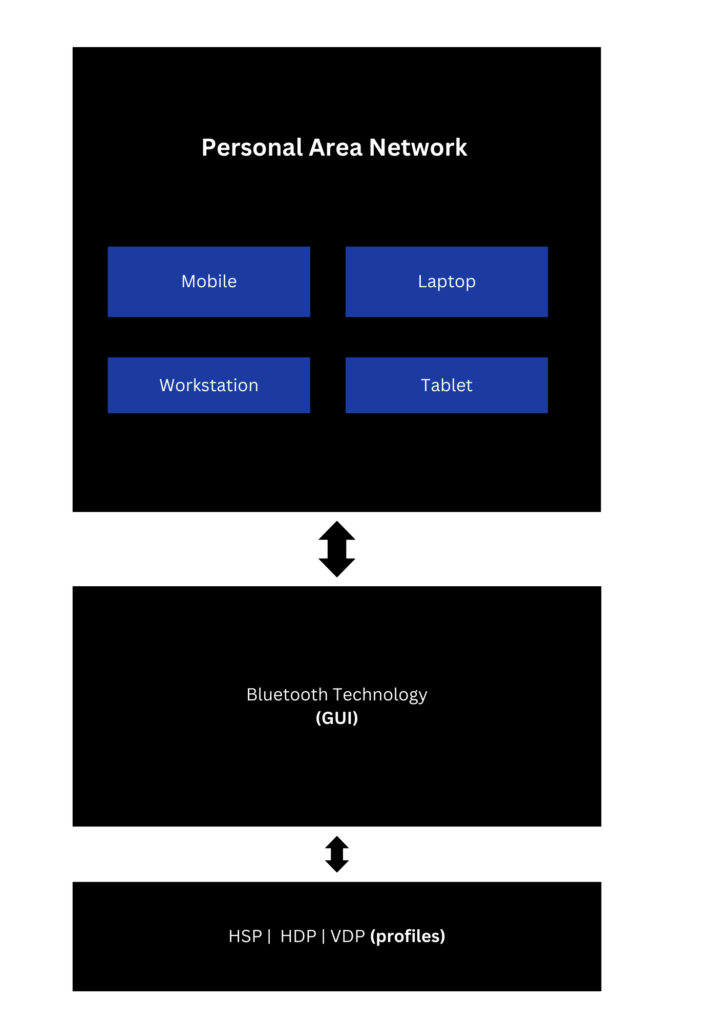
Bluetooth is a communication standard that assists in sharing data over small distances, Bluetooth-connected devices or Bluetooth device clusters are part of PAN (PERSONAL AREA NETWORK).
Bluetooth is utilized in all forms of application, the devices need to be paired to transfer data and communicate with each other.
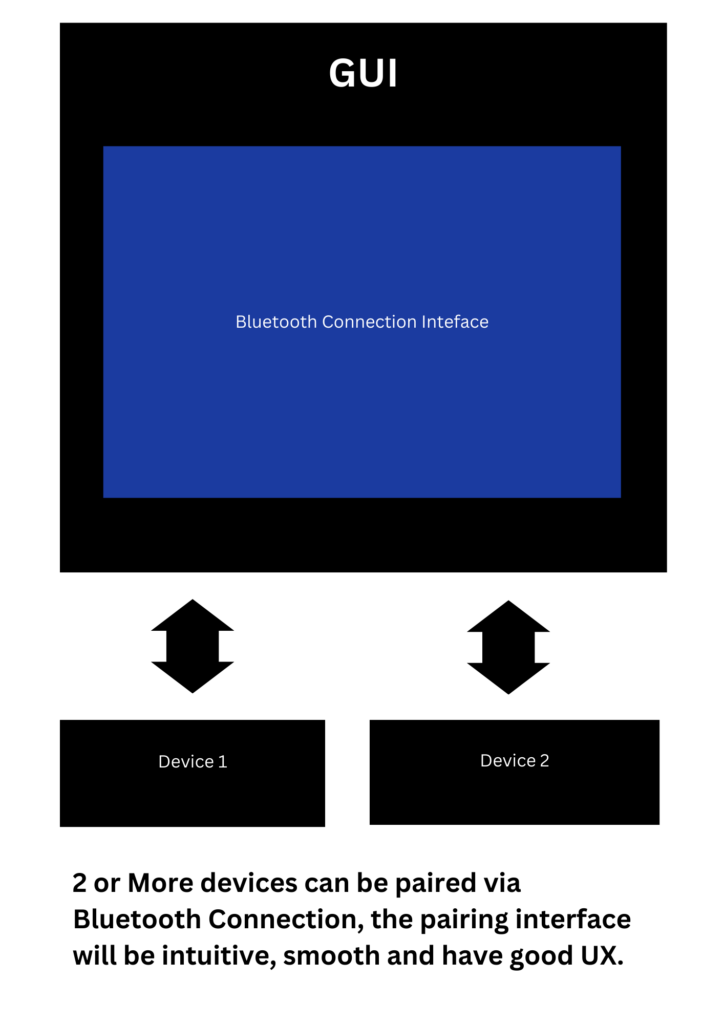
Bluetooth devices are paired with just a few clicks via a GUI-based authentication mechanism. The device pairing is an intuitive and easy process.
Bluetooth is the optimum solution for short-range voice and data communication, just pair the devices with Bluetooth and the data transfer and communication will be synced, Bluetooth as described earlier is a WPAN technology, which is leveraged for data exchange over small distances of a few meters.
The range of Bluetooth connection is around 10 meters, the devices that are connected need to be in proximity range to connect and share data. Usually, the GUI provided by the device vendor will be able to detect all the Bluetooth-enabled devices, and once the device is discovered then pairing request will be sent to another device and a Bluetooth connection can be established.
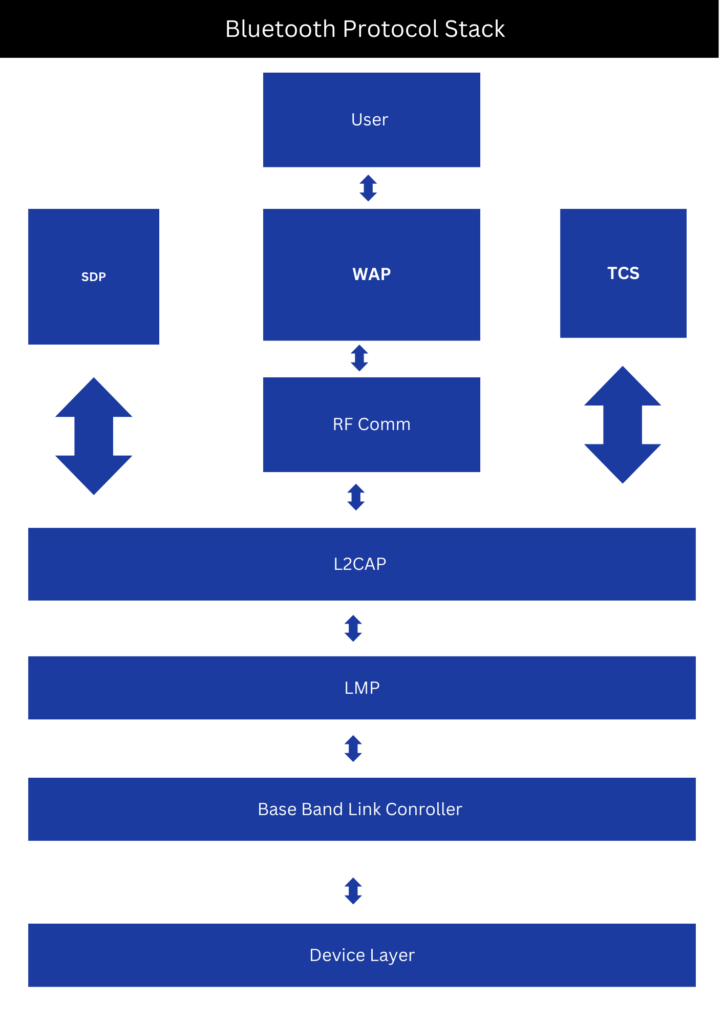
Bluetooth utilizes different RF bands, it leverages UHF between 2.402 GHz to 2.48 GHZ. Here are some of the commonly adopted protocols implemented with Bluetooth.
PPP (point-to-point protocol)
IP (internet protocol)
UDP (user datagram protocol)
TCP ( transmission control protocol)
WAP (Wireless application protocol)
The data rate can be up to 24 Mbps in Bluetooth low-energy (BLE)
Different versions of Bluetooth are available here are the core differences between them.
1) Bluetooth V2.1
2) Bluetooth 4.0 (LE)
3) Bluetooth 5 (LE)
BLUETOOTH v2.1: Range Upto 100M , 0.7 – 2.1 Mbit/s throughput, Scatternet topology
Bluetooth 4.0 (LE): Range up to 100m, 305 Kbit/S throughput, mesh network topology
Bluetooth 5 9 (LE): Range up to 400m, 1,369 Kbit/s throughput, mesh network topology
The 3 sets of Bluetooth technology fall under IEEE 802.15.1 standards. The use case for each Bluetooth technology is different, as bluetoothV2.1 consumes more power than Bluetooth 4LE, and Bluetooth 5 LE has a low energy profile.
Bluetooth V2.1 Use cases
Wireless speakers
Wireless headset
File and data transfer
Wireless printers
Wireless
Bluetooth 5-4
Medical devices
Biomedical sensors
Remote Controllers
Industrial sensors
IOT
Diagrams
The article above is rendered by integrating outputs of 1 HUMAN AGENT & 3 AI AGENTS, an amalgamation of HGI and AI to serve technology education globally.